Consensus-based clustering and data aggregation in decentralized network of multi-agent systems
Joshua Julian Damanik, Ming Chong Lim, Hyeon-Mun Jeong, Ho-Yeon Kim, Han-Lim Choi
Abstract
Multi-agent systems are promising for applications in various fields. However, they require optimization algorithms that can handle large number of agents and heterogeneously connected networks in clustered environments. Planning algorithms performed in the decentralized communication model and clustered environment require precise knowledge about cluster information by compensating noise from other clusters. This article proposes a decentralized data aggregation algorithm using consensus method to perform COUNT and SUM aggregation in a clustered environment. The proposed algorithm introduces a trust value to perform accurate aggregation on cluster level. The correction parameter is used to adjust the accuracy of the solution and the computation time. The proposed algorithm is evaluated in simulations with large and sparse networks and small bandwidth. The results show that the proposed algorithm can achieve convergence on the aggregated data with reasonable accuracy and convergence time. In the future, the proposed tools will be useful for developing a robust decentralized task assignment algorithm in a heterogeneous multi-agent multi-task environment.
Highlights
This paper presents a decentralized data aggregation algorithm using consensus methods tailored for multi-agent systems in clustered environments. It introduces a trust value to accurately aggregate COUNT and SUM metrics across clusters with minimal communication. The algorithm is designed to optimize performance in large, sparsely connected networks with low bandwidth, allowing agents to reach consensus efficiently. The findings indicate promising results for decentralized task assignments in complex, heterogeneous networks.
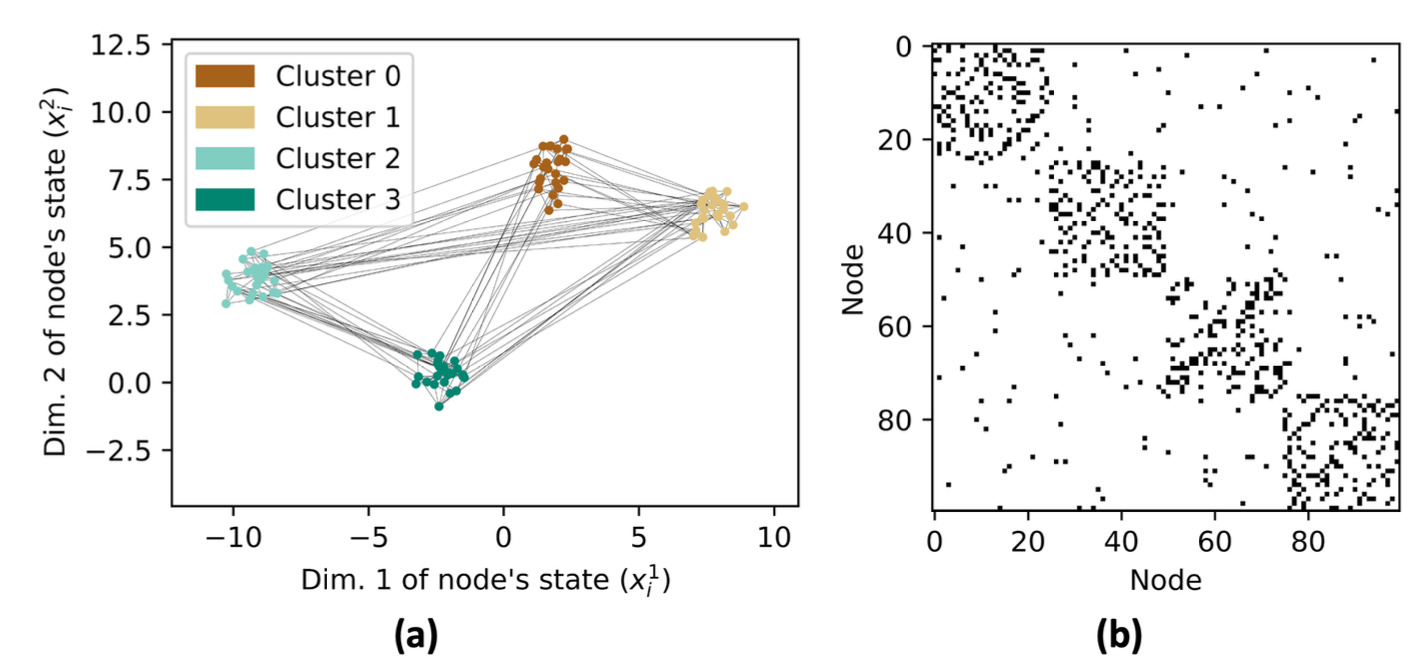
Figure 1: A neetwork consisting of 100 heterogeneous agents with 4 categories (a). The corresponding
adjacency matrix is shown in (b).
Key Contributions
- Decentralized Aggregation: Novel algorithm for COUNT/SUM data aggregation using trust-based consensus, suitable for clustered and heterogeneous networks.
- Trust Value Integration: Trust values improve aggregation accuracy and limit the impact of noise and inter-cluster communication.
- Efficiency in Sparse Networks: Algorithm achieves accurate aggregation with limited bandwidth and quick convergence, even in large multi-agent networks.
- Future Applications: Potential for developing robust decentralized task assignment and coordination algorithms in complex multi-agent systems.
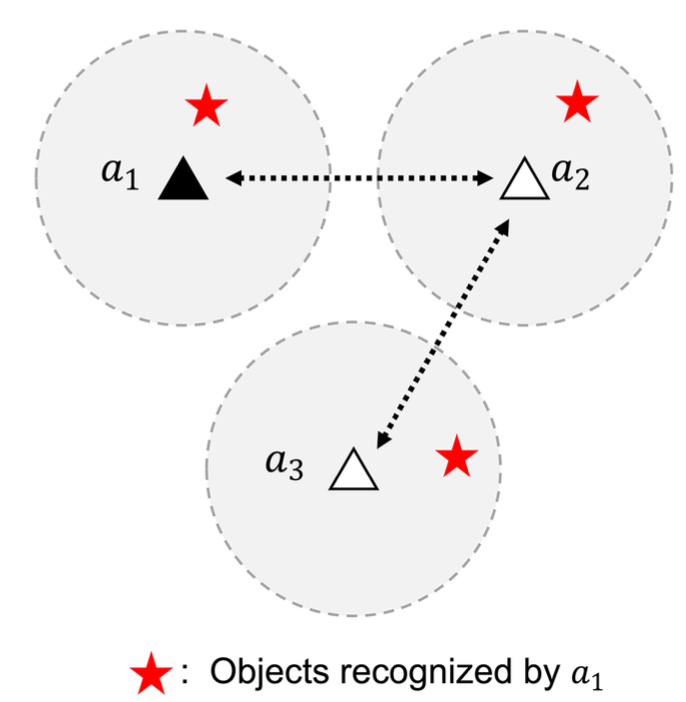
Figure 2: A problem of identifying objects in a decentralized network of multi-agent systems. Data
aggregation enables agent 1 to recognize objects beyond its sensor range.
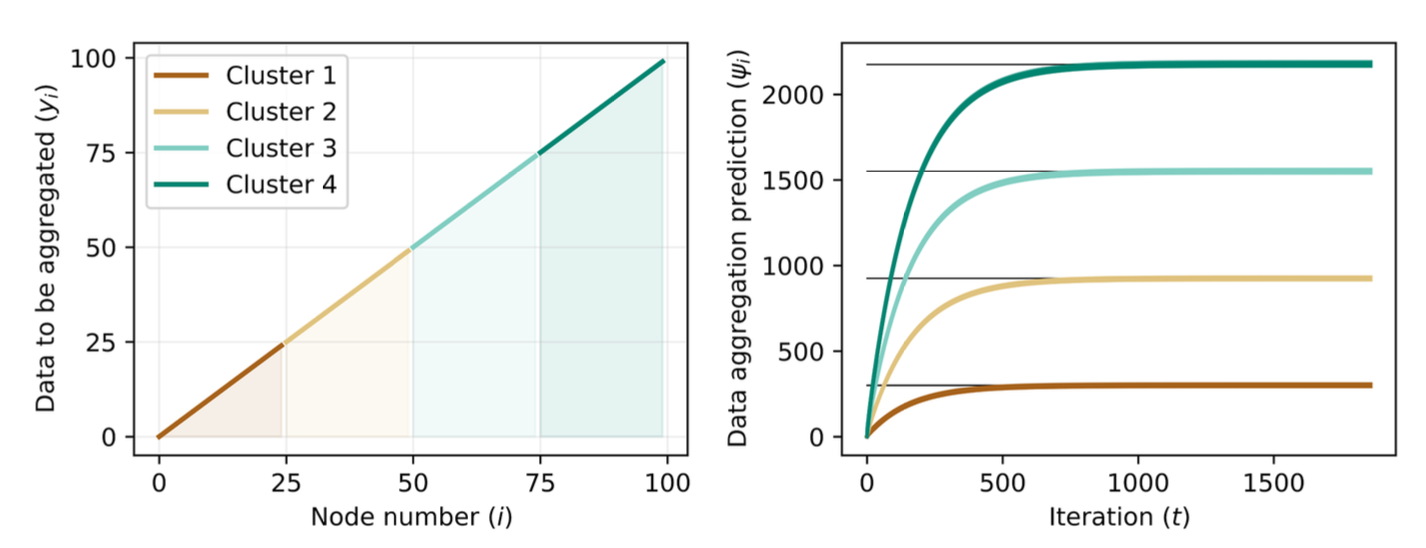
Figure 3: Data to be aggregated (a) for each nodes equals to the ID of each agents (yi; i) and the
data aggregation (b) converges to the sum of data to be aggregated of all agents in the same cluster,